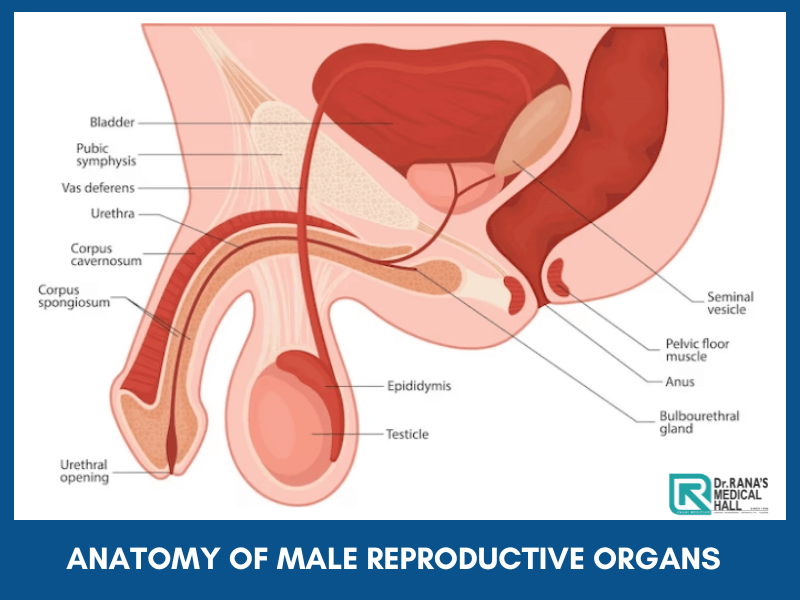
Anatomy of Male reproductive organs
Understand The Anatomy of Male reproductive organs
Parts of the Male Reproductive System
Anatomy of Male reproductive organs or the male reproductive system includes the penis, scrotum, and testicles. Most of these parts of the male reproductive system are situated outside.
Penis
Penis is the chief male reproductive organ used for and engaged in sexual intercourse with the female.
This has mainly three parts:
1. The root which is fixed to the abdominal wall
2. The body or shaft which is the cylindrical trunk of the penis
3. The glans or head, which is the cone-shaped part at the end of the penis.
The glans are covered with loose skin called the foreskin, which in some people will be removed by a procedure called Circumcision.
This is the male organ used in sexual intercourse.
Sensitive nerve endings can be seen at the glans. The tip of the penis is where Urethra, the tube that transports semen and urine is situated.
The penile body is three-chambered and cylindrical shaped. When a male is sexually aroused blood flow to large spaces in the chambers which are made of sponge-like tissue. As a result, the penis becomes rigid and gets ready for penetration during sexual intercourse. The elastic-natured foreskin tunes to the changes of the penis.
Scrotum
Scrotum is a pouch-like skin hanging below the penis, which contains testicles or testes, along with several blood vessels and nerves. The scrotum functions like a temperature control system for the testes. The testes usually need a temperature lesser than the body temperature. Muscles on the wall of the scrotum help the testicles to acquire the necessary temperature by moving close or away from the body
Testicles
Testicles are olive-like organs in the scrotum, guarded by the Spermatic chord, which makes testosterone, the male reproductive hormone, and generates sperms. The coiled tubes called Seminiferous tubes within the testes are responsible for creating sperm cells.
The internal organs of the male reproductive system, also called accessory organs, include the following:
Epididymis
A long, coiled tube that rests on the backside of each testicle and stores and transports sperm cells that are produced in the testes is the Epididymis. It also gets the immature sperms that emerge from the testes, which can only compete to fertilize to mature. It also is the job of the epididymis to bring the sperm to maturity, since the sperm that emerge from the testes are immature and incapable of fertilization.
Vas deferens
The vas deferens is a long, muscular tube that travels from the epididymis into the pelvic cavity, to just behind the bladder. The vas deferens transports mature sperm to the urethra, the tube that carries urine or sperm outside of the body, in preparation for ejaculation.
Seminal vesicles
The seminal vesicles are sac-like pouches that attach to the vas deferens near the base of the bladder which provides energy to the sperms to move by producing fructose.
Ejaculatory ducts
Vas deferens and the Seminal vesicles combine to form an Ejaculatory Duct.
Urethra
The urethra is the urine carrier. It carries the urine to the outside. But, it has an additional function of ejaculating semen, after attaining orgasm during sexual intercourse. It also blocks urine when the penis is erect, thereby allowing a smooth sexual interaction.
Prostate gland
The prostate gland is positioned below the urinary bladder in front of the rectum. This walnut-sized structure nourishes the sperm by contributing additional fluid.
Cowper’s glands
These are pea-sized structures located on the sides of the urethra just below the prostate, which produce a clear, slippery fluid that goes into the urethra. This fluid neutralizes the acidity caused by residual drops of urine, found in the Urethra.
Production, maintenance, and transportation of sperm and semen is the chief purpose of male reproductive organs. Along with this, the male reproductive system discharges the sperm within the female reproductive tract. Apart from these, it produces the hormones to maintain the full reproductive system.
Hormones determine the entire reproductive function. The three main hormones are
the Follicle-stimulating hormone, Luteinizing hormone, and Testosterone.
Follicle-stimulating hormone is necessary for sperm production (spermatogenesis), and luteinizing hormone stimulates the production of testosterone, which is also needed to make sperm. Male characteristics like muscle mass and strength, fat distribution, bone mass, facial hair growth, voice change, and sex drive are regulated by testosterone.
Consult Now to know more about the Anatomy of Male reproductive organs
Hope the Anatomy of Male reproductive organs is clear now. For more details, doubts, and information, Call/ WhatsApp now at 📞 (91) 8848511462 to book a consultation with Dr. Althaf Ibrahem Rana, the best Sexologist in Kerala.